SUV Dental Service
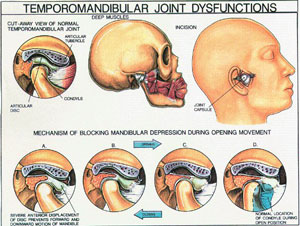
Temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJD or TMD), or TMJ syndrome, is an umbrella term covering acute or chronic inflammation of the temporomandibular joint, which connects the mandible to the skull. The disorder and resultant dysfunction can result in significant pain and impairment. Because the disorder transcends the boundaries between several health-care disciplines — in particular, dentistry and neurology — there is a variety of treatment approaches.
Signs and symptoms
Temporomandibular Joint Disorder may vary in their presentation and can be very complex, but are often simple. On average the symptoms will involve more than one of the numerous TMJ components: muscles, nerves, tendons, ligaments, bones, connective tissue, and the teeth. Ear pain associated with the swelling of proximal tissue is a symptom of temporomandibular joint disorder.
Symptoms associated with TMJ disorders may be:
- Biting or chewing difficulty or discomfort
- Clicking, popping, or grating sound when opening or closing the mouth
- Dull, aching pain in the face
- Earache (particularly in the morning)
- Headache (particularly in the morning)
- Hearing loss
- Migraine (particularly in the morning)
- Jaw pain or tenderness of the jaw
- Reduced ability to open or close the mouth
- Tinnitus
- Neck and shoulder pain
Treatments for TMDs
Depending on the diagnosis of the problem, a variety of treatments maybe recommended.
Phase I therapy is directed towards elimination muscle spasm. TMJ swelling, discoloration and reducing pain.
Phase II therapy aims to correct any discrepancy between the upper and lowerjaw.
- Occlusal equilibriation
- Splint/jaw repositioner appliance
- Muscle stimulant/ultrasound
- Orthodontic treatment
- Surgery
Conservative Treatment
Since the teeth, jaw joints and muscles can all be involved, conservative treatment for this condition varies. Typically, treatment will involve several phases. The first goal is to relieve the muscle spasm, pain, and inflammation. Then the specialist must correct the way the teeth fit together. This is accomplished by a removable device known as an orthotic/splint which is worn over the lower teeth until the bite is stabilized.
Along with the orthotic the specialist may also recommend:
- Exercise therapy
- Physical therapy
- Massage therapy
- Use of muscle relaxants
- Physical therapy modalities
Prevention
Better than having to go through these treatment modalities, or suffering the effects of temporomandibular joint disorders in the first place, you can prevent injury TMJ by adapting these eating habits:
- Chew food evenly on both sides of the mouth
- Avoid clenching, gritting and grinding your teeth
- Avoid chewing gum or tobacco.
- Avoid nuts and other hard or tough foods.
